What Is Bipolar Disorder?
Bipolar disorder is a term that is well known and is commonly used to describe someone that is acting unnaturally or different than usual. But most people don’t really know how to tell if someone has bipolar disorder.
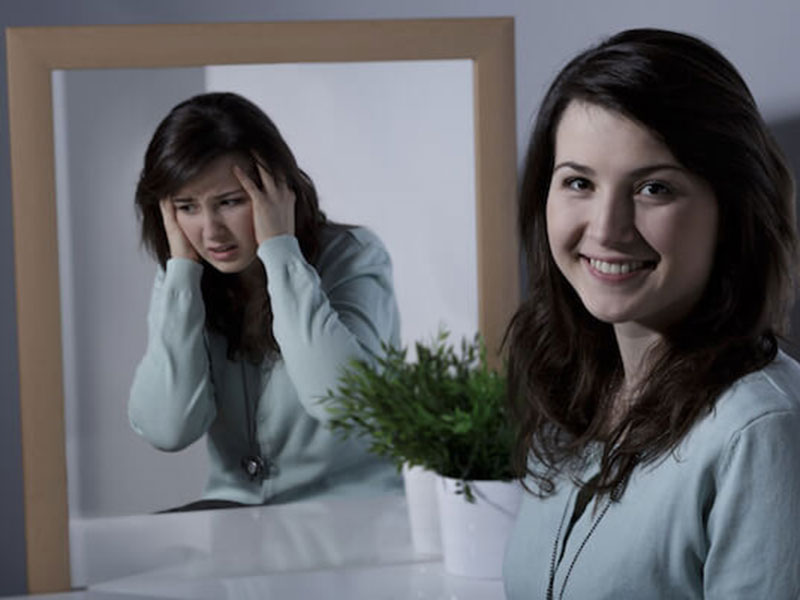
Bipolar disorder used to be called manic depression. It causes mood swings which involve emotional highs, called mania and hypomania, and emotional lows, called depression.
Attitude Alterations
The most noticeable and well-known effect of bipolar disorder is a change in attitude. The patient might suffer from mania, a feeling of euphoria and full of energy or depression, a feeling of sadness and hopelessness. The mood of someone with bipolar disorder might change as frequently as several times a week or as infrequently as a few times a year.
Types of Bipolar Disorder
To help the proper diagnosis of bipolar disorder and other related disorders, the American Psychiatric Association published the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). This manual describes the characteristics of the types of bipolar disorder.
For a patient to be diagnosed with bipolar I disorder, they must have had at least one manic episode which may precede or follow a hypomanic or major depressive episode. The symptoms of mania have the ability to cause significant impairment in life and may require hospitalization or cause psychosis, triggering a break from reality.
A patient diagnosed with bipolar II disorder must have had at least one major depressive episode that lasted at least two weeks and one hypomanic episode that lasted at least four days. They also must have never had a manic episode. The drastic and unpredictable changes in mood and behavior or major depressive episode has the ability to cause distresses and difficulty in other areas of life. The name may make it seem like bipolar II disorder is a milder form of bipolar I disorder, but it’s actually a completely separate diagnosis.
To be diagnosed with cyclothymic disorder, a patient must have had at least two years of numerous periods of hypomania symptoms, a less severe episode than a hypomanic episode. For children or teenagers, they must have at least one year of numerous periods of hypomania symptoms. They must also have a period of experiencing depressive symptoms, symptoms that are less severe than a major depressive episode. The symptoms of cyclothymic disorder are present at least half of the time and never go away for more than two months.
The Difference Between Manic and Hypomanic Episodes
While they sound alike and are somewhat similar, there are differences between manic and hypomanic episodes. A manic episode occurs when a person has an abnormally elevated, expansive, and/or irritable mood for a period of time. Typically, these last for about a week but can be less than that if they need to be hospitalized. To be a manic episode, the mood change must be severe enough to cause problems at work, school, or in social activities.
A hypomanic episode is where a person has an abnormally elevated, expansive, and/or irritable mood for least four consecutive days. Like with a manic episode, the change in mood must be noticeable to others but not sever enough to cause significant difficulty at work, school, or in social activities.
From a treatment perspective, the difference is that a manic episode will require hospitalization or a break from reality to prevent any harm to the patient or others while a hypomanic episode doesn’t require hospitalization or a break from reality.
Causes of Bipolar Disorder
While advances in science continue to allow researchers to learn more and more about bipolar disorder, the causes are still widely unknown. What scientists do know is what part of the body the causes of the disease come from. Those with bipolar disorder appear to have physical changes in the brain and an imbalance in the naturally occurring brain chemicals, called neurotransmitters. Research has also shown that the disease is more common in patients that have a first-degree relative that also has the condition.
Bipolar disorder is a disease that can have a major impact on a person’s life. Their rapid change in mood can cause difficulties at work, school, and in social activities and relationships. While there have been great advances in the knowledge of bipolar disorder, there is still a great deal unknown about the disease. But knowing the basics of the disease will help people better understand those that suffer from it.