May Is World Stroke Month
According to the American Stroke Association, someone has a stroke every 40 seconds within the United States. The month of May is World Stroke Month, and it’s a time to spread awareness about strokes, one of the top killers and causes of long-term disability. A recent survey showed that only about 8% of individuals actually know the most common stroke warning signs. Anyone can have a stroke, and it’s important for more people to recognize the warning signs, since every second counts when someone has a stroke. Here’s a closer look at strokes, how to recognize a stroke, and some suggestions for preventing strokes.
What Is a Stroke?
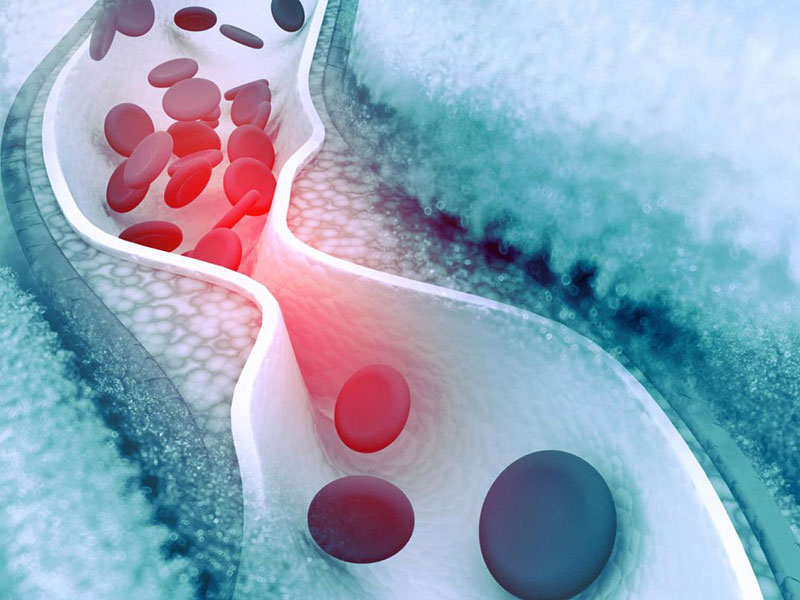
A stroke takes place when the blood flow to part of the brain is cut off. When this occurs, the brain cells don’t get enough oxygen, and they start to die. In some cases, a stroke may cause the permanent loss of memory, movement, and speech. Strokes are considered medical emergencies, and it’s essential to get prompt treatment to minimize complications and brain damage.
How to Recognize a Stroke
Thousands of people die every year from strokes, and more are left with disabilities after having a stroke. Learning the warning signs of a stroke can help you save a life. Some of the common signs and symptoms of a stroke include:
- Headache – A severe, sudden headache that often comes with altered consciousness, vomiting, or dizziness can indicate a stroke.
- Difficulty Speaking and Understanding – Confusion may occur and individuals may slur their words or have a tough time understanding speech.
- Problems Seeing – Blackened or blurred vision may occur in one eye or both eyes or double vision may occur.
- Difficulty Walking – Sudden loss of coordination or balance may occur, causing difficulty walking and stumbling.
- Numbness or Paralysis of the Face, Leg, or Arm – Numbness or paralysis may suddenly develop in the face, leg, or arm, particularly on one side of the body.
A very easy way to identify and remember common stroke symptoms is FAST. Use this to remember the early warning signs:
- F – Face – Have the individual smile. Is one side of their face drooping?
- A – Arms – Have the individual raise both of their arms. Is one arm drifting downward?
- S – Speech – Have the individual repeat a simple sentence. Note any strange or slurred speech.
- T – Time – If any of these symptoms are observed, it’s important to call 9-1-1 right away!
Preventing Strokes
While some of the risk factors for stroke cannot be controlled, lifestyle risk factors are controllable. Improving lifestyle risk factors can affect medical risk factors as well, helping you prevent a stroke in the future. Some of the risk factors you can change to reduce your risk of stroke include:
- Diet and Nutrition – Eating a healthy diet can reduce your risk of chronic diseases, reduce the risk of stroke, and improve overall health. Healthier eating habits involve eating whole grains, various high protein foods, low-fat dairy, and a variety of veggies and fruits. You should limit trans fats, sodium, added sugars, and saturated fats.
- Regular Physical Activity – Getting your body moving is important for stroke prevention. Studies show that exercising at least five times a week significantly reduces your risk of a stroke. Work to get at least 150 minutes of moderate intensity physical activity per week, as well as a couple days of muscle-strengthening activity.
- Reduce Alcohol Use – Many studies have shown a link between alcohol use and stroke. Drinking too much may increase blood pressure, increasing stroke risk. If you drink, do so in moderation. Men should have no more than two drinks each day, and women should have no more than one per day.
- Tobacco Use – Individuals who smoke have double the risk of having a stroke. Smoking can thicken the blood, increase plaque buildup in arteries, and increase clot formation. Quitting can significantly reduce your risk of a stroke. Talk to your physician about smoking cessation aids, such as medications, patches, programs, and/or counseling.
Although many people think that strokes only affect elderly individuals, strokes can happen to anyone, even young people and children. Taking measures to prevent stroke is important, but it’s also essential to understand and recognize stroke symptoms. When a stroke is recognized quickly and treated, individuals have a greater chance of getting the treatment they need to save brain tissue and help prevent long-term disability. Talk to your doctor today about your risk of stroke and what you can do to lower your risk.