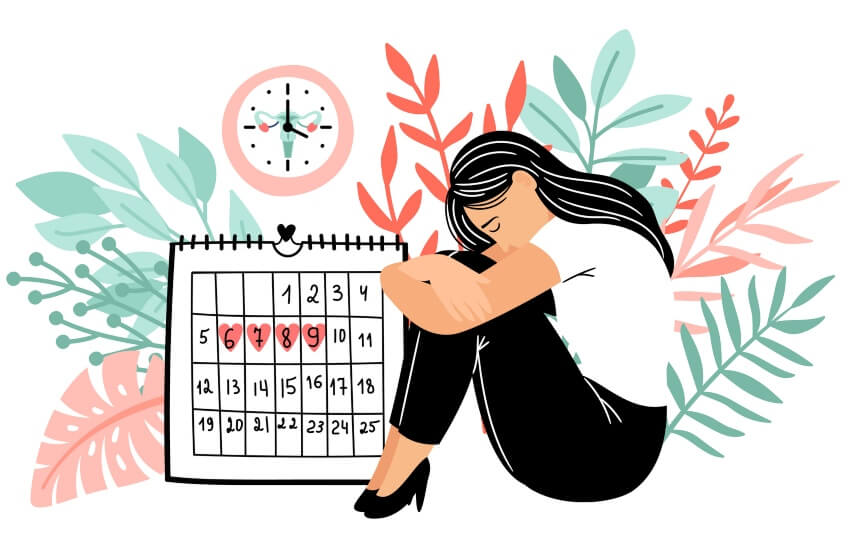
Abnormal Menstrual Periods
Many individuals will experience bothersome symptoms, irregular vaginal bleeding patterns and excessive bleeding at some point during their reproductive years. This can be a very frustrating and confusing experience, especially if you don’t know what’s going on. In this article, we will discuss the most common types of abnormal periods, as well as what you can do to manage them.
What Is a Normal Period?
Normal periods happen when hormones as produced by the brain, which sends a message to the ovaries to mature and release an egg, in preparation for a possible pregnancy. At this same time, the lining of the uterus begins to thicken, in order to make a healthy place for that egg to attach if it is fertilized by sperm. If the egg is not fertilized, the hormone levels change again, and that triggers the lining of the uterus to flush out through the vagina, which is known as menstruation, or a period.
This process usually starts between the ages of 11-14. Normally, there is a predictable amount of type between menstrual cycles, which on average is about 29 days, but can vary from 21-38 days, depending on the person. Even within the same person, cycles can vary 4-5 days from month to month, which is why sometimes it may seem that your period is coming slightly late or slightly early. It is normal to bleed anywhere from 4-8 days, with the heaviest days usually coming on the first few days of the cycle. The normal amount of bleeding can vary, but heavy bleeding is considered if it is necessary to change a pad or tampon more than every 3 hours.
PMS Symptoms
Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) is a group of symptoms that can occur during the days leading up to a menstrual cycle period. Symptoms can include mood swings, bloating, fatigue, and changes in appetite. PMS can be caused by the rapid hormonal changes that trigger your cycle. These changes are common, but some people experience them much more strongly than others. If symptoms are mild, they can often be addressed with changes in lifestyle, exercise and diet. If severe, you may need to talk to your medical provider about treatments that can alleviate these symptoms. If you are dealing with abnormal PMS symptoms, know that you are not alone. There are many resources available to help you manage your symptoms and feel your best.
Types of Abnormal Periods/Irregular Menses
Types of abnormal periods, and their corresponding causes and symptoms, include:
1. Heavy or Prolonged Periods (Menorrhagia)
If your period lasts for more than 8 days or you are having to change a pad or tampon more than every 3 hours, this may cause you to lose too much blood and lead to anemia. You may experience headaches, fatigue, shortness of breath, or dizziness/lightheadedness. It is important that you seek treatment to help regulate your cycle and reduce the amount of blood loss.
2. Bleeding Between Your Periods
Bleeding between periods, also called spotting, is light bleeding that occurs outside of your regular menstrual cycle. It can occur at any time during the month and is usually caused by something minor, like an infection or hormone imbalance.
3. Dysmenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea is a common problem for women. It is the pain and cramps that some women experience before and during their menstrual periods. The pain can be so bad that it interferes with daily activities. Symptoms of dysmenorrhea include pain in the lower abdomen, back, and thighs. The pain may be so bad that it interferes with daily activities. Women may also have nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The pain may last for a few hours to a few days.
Causes
There are many different causes of irregular menstrual bleeding. Some common causes include:
- Hormonal imbalances: This is one of the most common causes of irregular bleeding. Hormonal imbalances can be caused by a variety of factors, including medication, pregnancy, thyroid problems, PCOS, weight changes, peri-menopause (the years just before your periods stop), and stress.
- Uterine abnormalities: Uterine abnormalities, such as fibroids or polyps, can also cause abnormally heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding.
- Infections: Infections of the reproductive organs, such as a sexually transmitted infection or urinary tract infection, can also lead to abnormal cycles
- Blood clotting disorders: Blood clotting disorders, such as Von Willebrand disease or hemophilia, can also cause excessive bleeding during menstrual periods.
- Pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy, or miscarriage: Often in the early stages of pregnancy, spotting or bleeding can occur that may be mistaken for an abnormal menstrual cycle. This can be normal, but can also be a sign of a problem with the pregnancy that needs to be addressed. If you are sexually active and have an irregular cycle, it is important to take a pregnancy test or visit your doctor’s office for a pregnancy test.
- Cancer: Uterine and cervical cancer are rare but serious conditions that can cause irregular bleeding. It is important to stay up to date on your pap smear for cervical cancer screening and to be evaluated if abnormal bleeding patterns occur.
4. Amenorrhea/Missed Menses
Amenorrhea is a condition that results in the absence of menstruation. There are two types of amenorrhea: primary and secondary. Primary amenorrhea is when someone has not started menstruation by age 16, secondary amenorrhea is when someone has been having normal periods, then misses a cycle for three months or more. It is quite normal to miss a period every once in a while due to stress, illness, or other factors, but not having a period for more than 3 months can lead to other health issues, and it is important to seek care to help determine why this is the case.
Causes
- Pregnancy
- Hormone imbalances like thyroid disorder or polycystic ovarian syndrome
- Menopause
- Problems with the reproductive organs
- Genetic abnormalities
- Stress: when your body feels stressed, it often stops normal cycles to conserve energy. Talk to your provider about ways to reduce stress, or try meditation, yoga, or seeing a counselor.
- Low body weight, eating disorders, excessive exercise: all these will decrease your body’s ability to produce normal hormones and can stop the menstrual cycle. It is important to give your body the fuel it needs to maintain all metabolic functions
- Marijuana use: this can interrupt the hormonal signaling in the brain that triggers menstrual cycles. If you need help cutting back on or stopping marijuana use, contact your healthcare provider.
5. Uterine Bleeding After Menopause
Menopause usually happens between the ages of 45-55. Once periods have stopped for a full year, this is considered menopause. If you have vaginal bleeding at any point after menopause, this is abnormal and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Causes
There are many potential causes of uterine bleeding after menopause, including:
- Hormonal imbalances: After menopause, the ovaries no longer produce estrogen. This can cause a hormonal imbalance, which can lead to irregular periods and uterine bleeding.
- Medications: many women taking blood-thinning medications may experience vaginal bleeding after menopause, but it is still important that you have this evaluated to ensure there are no other abnormalities
- Uterine structural changes: These are noncancerous growths or thickening of the endometrial lining that can develop in the uterus and cause bleeding even after menopause.
- Cancer: Uterine and cervical cancer are rare but serious conditions that can cause uterine bleeding after menopause.
Contact Your Healthcare Provider if You Are Experiencing Abnormal Periods
If you are having abnormal periods, then it is important to contact your family or gynecologic medical provider. Periods can be irregular for a variety of reasons, some of which are benign and others that could be indicative of a more serious health issue. Your provider will be able to help you determine the cause of your abnormal periods and will provide you with the appropriate treatment. Brevard Health Alliance in Florida can help connect you to the services you need. Contact us today to schedule an appointment!