Women’s Heart Health and Diabetes: A Closer Look
Research suggests that people living with diabetes have more than a two times greater chance of developing heart disease than those who do not. Furthermore, women with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing cardiovascular problems when compared to men.
With this alarming statistic in mind, it’s important that women understand this powerful connection and prioritize diabetes management. Research indicates that nearly 45% of women were unaware of their risk for heart disease. In addition, prediabetes and diabetes in their early stages may not yet cause symptoms, leaving many women unaware of their condition or their risk for poor cardiovascular health.
While these statistics can be alarming, simple lifestyle modifications and regular check-ups can help you to stay on top of your health proactively. In this article, we’ll share more about the important connection between heart health and diabetes and how you can take control to help prevent and manage these conditions.
Understanding the Connection Between Heart Health and Diabetes
For women who have diabetes, it is crucial to understand the clear connection between this condition and an increased risk for heart problems. Since type 2 diabetes often leads to regular high blood sugar levels, this increased blood glucose can impact the body’s red blood cells. High blood glucose can restrict the flow of oxygen throughout the blood, raising the risk for cardiovascular problems in women.
Regular testing for blood glucose levels, such as a three-month A1c test is important for keeping a close eye on blood sugars. According to the American Academy of Cardiology, a person with diabetes has a two to four times higher risk of developing coronary artery disease (CAD).
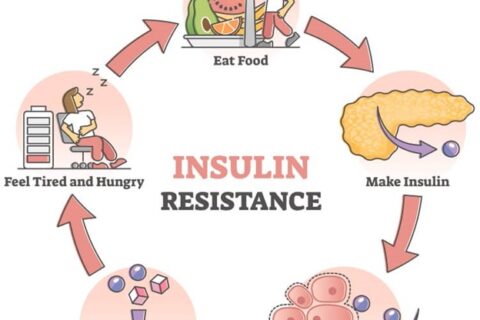
Insulin Resistance & Metabolic Syndrome
People with type 2 diabetes have a condition known as insulin resistance, where cells in the body no longer respond to changes in blood sugar. This insulin resistance plays a negative role in your heart health, leading to increased A1c levels and a higher risk of developing heart disease (up to 18%).
Also known as insulin resistance syndrome, metabolic syndrome is also a serious concern for those with elevated blood sugar levels. This condition is a cluster of symptoms that raise a person’s risk for heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. People with metabolic syndrome often have high blood pressure, high blood glucose levels, and excess body weight.
Risk Factors
Many of the same risk factors that can put women at risk for type 2 diabetes are also risk factors for heart disease. Common risk factors for both conditions include obesity, high blood pressure, or living a sedentary lifestyle. Women who have already been diagnosed with Diabetes and have high blood pressure are at an elevated risk for heart disease.
Reducing these common risk factors of diabetes and heart disease is possible. For example, starting a regular exercise routine can improve your body’s ability to use insulin and absorb glucose. Furthermore, staying active can help you maintain a healthy body weight, reducing your risk for obesity. Research from the Harvard School of Public Health suggests that obesity can increase a woman’s risk for diabetes by 20 to 40 times when compared to a person of a normal body weight.
Lifestyle choices play a critical role in preventing and mitigating your risk for diabetes and heart disease. Regular exercise, along with avoiding consuming sugary and processed foods can reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. It is also important to limit your consumption of alcohol and red meat.
As a preventative effort, all adults ages 35 and up should have regular blood glucose testing, ordered by their doctor. Finding ways to manage stress effectively can also help keep your blood pressure in check, which can reduce your risk for type 2 diabetes as well.
Prevention and Treatment Strategies
Lifestyle modifications, such as diabetes medication and regular check-ups can help you to manage your diabetes and reduce your risk of heart problems. Some people with type 2 diabetes may need to take medication in order to reduce their blood sugar levels. Lifestyle interventions, along with a popular medication known as Metformin, reduced diabetes incidence dramatically in clinical studies.
Women with prediabetes or who have not yet been diagnosed can take an active role in preventing this condition by maintaining a healthy lifestyle. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the best diabetes prevention strategies include maintaining a healthy body weight, staying active, avoiding smoking, and eating a wholesome diet.
At Brevard Health Alliance (BHA), our women’s health and family care physicians work closely to help patients with diabetes manage their condition and monitor their heart health.
Call BHA at 321-361-4989 to schedule an appointment today.